
Nuclear reactors usually rely on uranium to fuel the chain reaction. The heat from nuclear fission is used to raise steam, which runs through turbines, which in turn power the electrical generators. With this heat, a coolant is heated as it is pumped through the reactor and thereby removes the energy from the reactor. In its central part, the reactor's core produces heat due to nuclear fission. The nuclear reactor is the heart of the station. The water-steam cycle corresponds to the Rankine cycle. The water is then pumped back into the steam generator and the cycle begins again. The condenser is a heat exchanger which is connected to a secondary side such as a river or a cooling tower. After the steam turbine has expanded and partially condensed the steam, the remaining vapor is condensed in a condenser. The pressurized steam is then usually fed to a multi-stage steam turbine. The reactor coolant then goes to a steam generator and heats water to produce steam. The coolant may be water or gas, or even liquid metal, depending on the type of reactor. The fission in a nuclear reactor heats the reactor coolant. The conversion to electrical energy takes place indirectly, as in conventional thermal power stations.
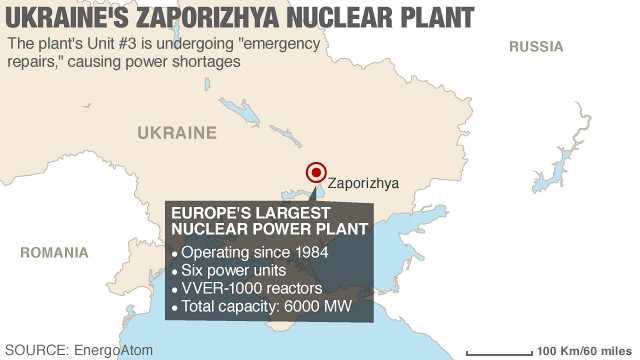
Despite some spectacular catastrophes, nuclear power plants are among the safest mode of electricity generation, comparable to solar and wind power plants. Nuclear power plants have a carbon footprint comparable to that of renewable energy such as solar farms and wind farms, and much lower than fossil fuels such as natural gas and coal. However, building a nuclear power plant often spans five to ten years, which can accrue to significant financial costs, depending on how the initial investments are financed. Nuclear plants are very often used for base load since their operations, maintenance, and fuel costs are at the lower end of the spectrum of costs. As of 2022, the International Atomic Energy Agency reported there were 422 nuclear power reactors in operation in 32 countries around the world, and 57 nuclear power reactors under construction. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity. A nuclear power plant ( NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
